Unlocking the Secrets of Your Gut Microbiome to Enhance Mental Health and Resilience
Discover how optimizing your gut microbiome can boost your mental health and resilience. Learn practical tips and science-backed insights to... Read more
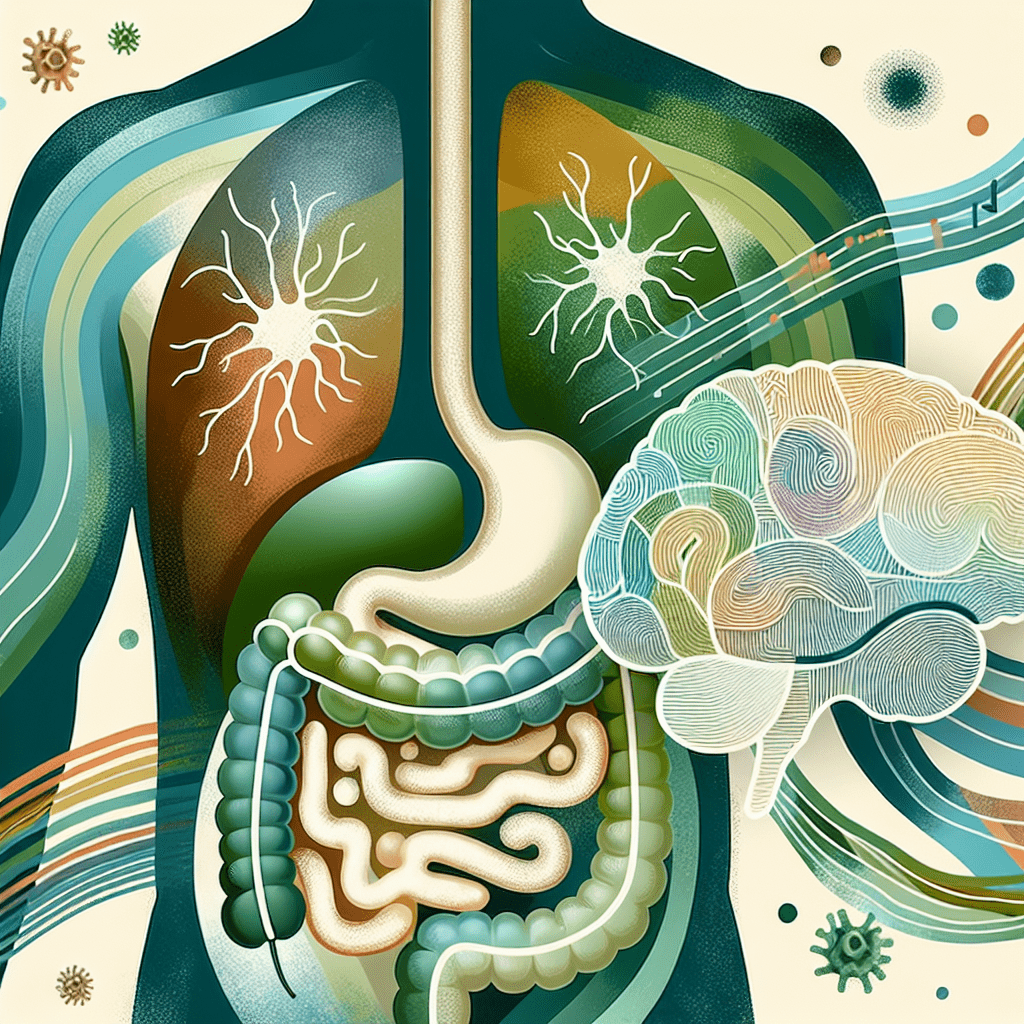
Discover how the gut-brain axis functions to link mood and digestion. This network operates through several channels: the vagus nerve that relays signals between gut and brain, microbial metabolites such as short-chain fatty acids and serotonin precursors, and immune cues that modulate inflammation and neural signaling. When you eat, stress, or sleep, these signals shift, and so can appetite, energy, and emotional tone. Understanding these gut-brain axis functions helps explain why a restless night can leave you overwhelmed with cravings, and why meals can boost or dampen mood in surprising ways. On the nervous-system side, the enteric nervous system acts like a second brain in the gut, coordinating motility and secretions. The autonomic nervous system and the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis translate stress and relaxation into gut responses, shaping permeability and microbial environment. The gut microbiota then feed back to the brain with compounds that influence mood, cognition, and stress resilience. In daily life, these dynamic signals mean that consistent sleep, balanced meals, and stress management can quietly strengthen the gut-brain axis functions that support both mood and digestion. InnerBuddies offers a white-label Gut Health Operating System that powers gut health testing products with a modular, scalable architecture. The Gut Microbiome Health Index provides a 0–100 score indicating overall gut health based on an exclusive IP deal with EAFIT University in Colombia. Bacteria Abundances cover a top 40 set, showing how you compare against a healthy cohort, while Bacteria Functions categorize metabolic activities as positive or negative and display your standing in each functional area. Target Group Analysis digs into pathways most relevant for groups such as Healthy Aging, Endurance Sport, Power Sport, and Skin & Hair Health. Personalization runs deep: nutrition advice uses 3‑day food diaries matched to stool data to tailor diet and probiotic/prebiotic recommendations to your unique gut microbiome. Learn more on the consumer side at the InnerBuddies microbiome test page, and keep momentum with the Gut Health Membership. For partners, the B2B page explains how to license or white-label the platform. To boost daily well‑being, start with practical steps that support gut-brain axis functions: eat a diverse mix of fiber-rich plants to feed beneficial microbes, include fermented foods like yogurt, kefir, sauerkraut, and miso, stay hydrated, and maintain regular meal timing. Prioritize sleep and stress management through mindfulness or gentle movement, as rest and calm signaling help balance autonomic tone. Regular physical activity can diversify the microbiome and improve gut motility, while a simple habit like recording three days of meals helps you see how specific foods affect digestion and mood. If you’re ready to explore how these insights translate into real-world testing and personalized plans, check out the consumer options or speak with a partner about bringing a gut health program to market.

Discover how optimizing your gut microbiome can boost your mental health and resilience. Learn practical tips and science-backed insights to... Read more